The MAR Ratio, also known as the Managed Account Ratio, is a financial metric used to evaluate the risk-adjusted performance of investments. This ratio provides insight by comparing an investment’s returns to its drawdowns, highlighting how well it manages risk. The formula is straightforward: the MAR Ratio divides the Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) by the Maximum Drawdown. This comparison offers a perspective on how much return an investment achieves relative to its largest loss or “drawdown.”
source: Roger Scott on YouTube
Used primarily with hedge funds, managed accounts, and high-volatility assets, the MAR Ratio is especially valuable in markets where drawdown risk is a key concern. In the simplest terms, it helps investors understand the stability of their investment’s returns. For example, a hedge fund that has a consistent CAGR but suffers only minor drawdowns will have a high MAR Ratio, indicating a strong risk-adjusted performance. Conversely, investments with high returns but substantial losses may have lower MAR Ratios, suggesting a higher-risk profile.

Why is the MAR Ratio Important?
The MAR Ratio has earned a respected place among performance metrics for a few reasons. Its focus on drawdowns—the peak-to-trough decline in an investment’s value—makes it ideal for risk-conscious investors. Unlike the Sharpe or Sortino Ratios, which consider return volatility and downside deviation, the MAR Ratio zeroes in specifically on maximum drawdown. This characteristic makes it an attractive tool for evaluating investments in hedge funds or managed futures, where avoiding substantial losses is often prioritized over maximizing returns.
But the MAR Ratio isn’t just for the pros. It’s equally useful for individual investors aiming to get a handle on how investments perform under stress. By helping you gauge risk-adjusted returns, the MAR Ratio supports more informed decision-making, allowing for an investment selection process grounded in risk management.
What is the MAR Ratio?
We’ll dive into the MAR Ratio’s practical uses and benefits. It will explore how the MAR Ratio is calculated, what it reveals about an investment’s risk management, and why it’s relevant in today’s investment landscape. By understanding the MAR Ratio, you can better interpret the stability and reliability of potential investments and make decisions that align with your risk tolerance.
The goal here is to give you a clearer understanding of this valuable metric so you can:
- Measure Risk Management: Evaluate investments in a way that prioritizes loss management.
- Interpret Performance: Identify investments that combine strong returns with lower drawdowns.
- Make Informed Decisions: Use data-driven insights to select investments with stable, risk-adjusted returns.
Incorporating the MAR Ratio into your investment analysis provides a fresh perspective on balancing return potential with risk exposure. Whether you’re navigating traditional stocks or venturing into more complex assets like hedge funds, understanding the MAR Ratio can elevate your approach to portfolio management.
Tip: While the MAR Ratio can guide your decision-making, remember to use it alongside other metrics. This way, you’ll have a more rounded view of an investment’s profile, covering both its risk and reward potential.
Calculating the MAR Ratio
The MAR Ratio Formula
The MAR Ratio formula is a relatively simple calculation. It’s designed to show the relationship between an investment’s growth and its risk. Here’s the formula:
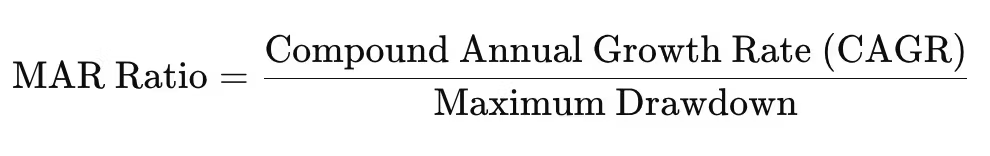
Each component of this ratio provides key insights:
- Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR): This represents the average annualized return on an investment over a specific period. CAGR smooths out the ups and downs, giving you a consistent growth rate to better assess performance.
- Maximum Drawdown: This is the largest peak-to-trough decline in an investment’s value over a given period. Maximum drawdown indicates the biggest loss suffered from a high to a low point, making it a crucial measure of risk.
The MAR Ratio, then, compares how much return an investment has achieved (CAGR) relative to its largest loss (maximum drawdown). A higher MAR Ratio is generally better as it indicates higher returns achieved with relatively lower exposure to losses.
Step-by-Step Calculation Example
To illustrate, let’s calculate the MAR Ratio with some example numbers.
Suppose you’re analyzing an investment that has achieved a CAGR of 12% over five years, with a maximum drawdown of 20% during that period.
Using the MAR Ratio formula:
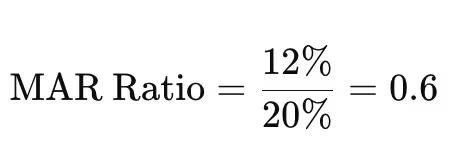
In this case, the MAR Ratio is 0.6. This means that for every unit of risk taken (in this case, measured by maximum drawdown), the investment achieved a return of 0.6 units. In general, a MAR Ratio above 0.5 is considered favorable in high-volatility investment environments, though the ideal number varies by asset type and investor risk tolerance.
Key Takeaways:
- A higher MAR Ratio suggests a more favorable risk-adjusted return. If you’re comparing investments and one has a MAR Ratio of 0.9 while another has 0.4, the first investment has performed better in terms of balancing return against risk.
- Understanding the impact of drawdown is essential. A high CAGR with high drawdown often indicates volatility, which could mean higher risk in turbulent markets.
Why a Higher MAR Ratio Matters
When looking at investment options, a higher MAR Ratio offers some reassurance about the quality of risk management. A MAR Ratio of 1 or above generally reflects an investment that achieved returns greater than its maximum drawdown, showing efficient risk-adjusted growth.
This metric is particularly useful in portfolios with high volatility. Hedge funds, for instance, frequently analyze the MAR Ratio because it highlights how well returns are sustained through market swings. For traditional investments, it can be equally revealing, especially in markets with high uncertainty where protecting capital becomes a priority.

How the MAR Ratio Assesses Risk Management
Evaluating Drawdown Risk with the MAR Ratio
The MAR Ratio is a straightforward yet powerful tool for understanding risk management in investments, especially for those focused on minimizing losses while seeking steady returns. By emphasizing drawdowns, the MAR Ratio sheds light on how much an investment might lose at its lowest point relative to its growth. This can be especially reassuring for risk-conscious investors looking to avoid major dips that could significantly impact their portfolio.
When an investment maintains a high MAR Ratio, it suggests that its returns are stable and consistent relative to the potential for loss. In other words, a high MAR Ratio indicates an investment that has successfully balanced growth with controlled risk. This is crucial in periods of market volatility when the main concern is not just earning returns but also protecting capital from significant downturns.
In practical terms, the MAR Ratio’s focus on drawdowns provides a unique view into an investment’s potential resilience. This ratio can help identify options that have shown effective risk management—investments that deliver returns while limiting periods of substantial decline. For risk-averse investors, a high MAR Ratio is a beacon, signaling a choice that has managed to dodge deep dips and generate growth steadily.
Comparing the MAR Ratio to Other Risk Metrics
While the MAR Ratio is effective for assessing drawdown risks, it stands alongside other popular risk metrics, each with a different emphasis on risk and return. The Sharpe Ratio, for instance, measures risk-adjusted returns by comparing an investment’s excess return to its standard deviation. This metric is widely recognized and works well for gauging volatility, but it may miss key details about maximum losses, especially in turbulent markets.
The Sortino Ratio also assesses risk-adjusted performance, but it specifically looks at downside deviation—meaning it focuses on negative fluctuations only, without penalizing positive volatility. The Sortino Ratio helps measure how well an investment does in generating returns while limiting downside risk, but it still does not give direct insight into the worst-case scenario for an investment, which is where the MAR Ratio shines.
The MAR Ratio’s specific focus on drawdown risk makes it particularly relevant for hedge funds and managed accounts, where large peak-to-trough losses can have an outsized impact on overall performance. This can be particularly important for assets in high-volatility markets, where large swings in value are common. Investments with a high MAR Ratio demonstrate a history of effective drawdown management, suggesting a level of stability that appeals to investors prioritizing consistent, risk-adjusted returns.
Key Differences Between the MAR Ratio and Other Metrics:
- Sharpe Ratio: Best for assessing general volatility across gains and losses but less effective for highlighting specific drawdown risks.
- Sortino Ratio: Focuses on downside risk but lacks insights into the worst-case drawdown an investment may experience.
- MAR Ratio: Unique in its emphasis on drawdowns, making it valuable for investments where major losses could severely impact overall performance.
Why the MAR Ratio is Valuable for High-Volatility Assets
The MAR Ratio is particularly helpful when assessing investments prone to high volatility or those managed with strategies that actively seek to control losses, like hedge funds. In these cases, the MAR Ratio offers an added layer of understanding by illustrating how well a fund or investment can manage worst-case declines. For high-volatility assets, a high MAR Ratio can act as a green light, signaling robust risk management even when faced with challenging market conditions.
By comparing different metrics, you gain a rounded view of an investment’s risk profile. However, when it comes to assessing risk through the lens of potential losses, the MAR Ratio offers a clarity that’s hard to beat. It’s an essential tool for those who seek growth but want to avoid large, potentially portfolio-altering losses along the way.
Interpreting the MAR Ratio in Investment Analysis
What a High MAR Ratio Means for Investors
A high MAR Ratio signals a valuable trait in any investment: high returns relative to its maximum drawdown. This implies that the investment has not only delivered notable growth but has also managed to avoid major declines. For risk-conscious investors, a high MAR Ratio is an encouraging sign. It suggests that the investment has achieved its gains while carefully managing downturns, leading to a strong risk-adjusted performance. In simpler terms, it’s an indicator that this investment could balance reward with a level of risk that’s been well contained.
Investments with a high MAR Ratio are generally more stable. They tend to provide consistent returns, making them attractive to investors who value steadiness in their portfolio. Such assets are often preferred during volatile times, as they have shown resilience in the face of market ups and downs. Rather than swinging wildly, they maintain a more stable performance, with controlled losses that protect capital in rough markets. For those who prioritize low volatility and preservation of capital, a high MAR Ratio becomes a key factor in choosing between investment options.
Moreover, a high MAR Ratio can also distinguish the best-performing funds or assets in a crowded field of investment choices. In fields like hedge funds or managed futures, where large drawdowns can severely impact an investor’s returns, the MAR Ratio offers a targeted lens to identify which investments manage risk effectively. In short, it’s a way to pinpoint investments that have mastered balancing growth and risk.
Key Highlights of a High MAR Ratio:
- Indicates high returns relative to drawdowns, suggesting well-managed risk.
- Appeals to investors focused on consistent, stable growth over time.
- Helps differentiate high-performing funds, especially in volatile markets.
Limitations of the MAR Ratio
Despite its strengths, the MAR Ratio has some limitations investors should consider. One key drawback is its reliance on historical performance. The MAR Ratio, like many metrics, is calculated using past data. This means it reflects how the investment performed in prior market conditions, which may not necessarily predict how it will respond to future events. For instance, an investment that showed resilience in one period may not have the same performance in an entirely different market environment, as factors influencing returns and drawdowns can change over time.
Another limitation lies in the MAR Ratio’s narrow focus on drawdowns and returns, which doesn’t account for other crucial risks. While it’s excellent for understanding risk-adjusted performance, it doesn’t consider factors like liquidity risk or credit risk. For example, an investment with a high MAR Ratio might appear strong but could still carry liquidity issues, meaning it may be difficult to sell or exit in certain market conditions. Similarly, credit risk—especially in debt or bond investments—is another consideration outside the MAR Ratio’s scope. It’s essential to remember that a high MAR Ratio alone doesn’t provide the full risk picture, so investors should always view it in the context of a broader analysis.
Important Considerations:
- Historical Focus: Past performance doesn’t always predict future results.
- Limited Scope: MAR Ratio doesn’t address liquidity, credit risk, or other financial health indicators.
- Complementary Analysis: Use alongside other metrics to gain a comprehensive risk assessment.
Tips for Using the MAR Ratio Effectively
The MAR Ratio works best when used as part of a multi-faceted approach to investment analysis. Investors can gain a more balanced understanding by combining the MAR Ratio with other risk metrics, like the Sharpe or Sortino Ratios, or by incorporating qualitative assessments of an investment’s strategy, market conditions, and management quality. Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Use alongside other metrics: To better gauge an investment’s overall health and risk profile.
- Focus on consistency: Look for investments that maintain a high MAR Ratio across different periods, suggesting robust performance.
- Consider the investment type: The MAR Ratio can be particularly useful for volatile assets or funds known for drawdown sensitivity, like hedge funds.

Practical Applications of the MAR Ratio in Portfolio Management
The MAR Ratio can be a game-changer for investors looking to make well-informed choices. By focusing on both returns and drawdown risks, this ratio provides a clear, risk-adjusted view of a fund’s performance. For those managing their portfolios or selecting funds, especially in areas like hedge funds and managed accounts, the MAR Ratio offers a valuable perspective.
Using the MAR Ratio for Fund Selection
When it comes to fund selection, the MAR Ratio allows investors to assess risk-return profiles more accurately. This metric helps in picking funds that not only deliver returns but also manage risks effectively. In essence, it’s about finding funds that yield significant growth without excessive downside.
For instance, if you’re comparing two funds with similar returns, the one with a higher MAR Ratio is likely to be more resilient against market drops. The MAR Ratio’s focus on drawdown helps highlight those investments that may not always deliver the highest returns but are less likely to incur substantial losses during turbulent times. In hedge fund investing, where large drawdowns can affect long-term wealth, this can be a critical differentiator.
Key Tips for Fund Selection with MAR Ratio:
- Compare MAR Ratios Across Similar Funds: When evaluating multiple funds, especially in the same asset class, higher MAR Ratios suggest better risk-adjusted returns.
- Focus on Long-Term Consistency: Funds that maintain a high MAR Ratio over time are often better managed and offer more stability.
- Consider MAR Ratio in High-Volatility Funds: In investments where drawdown risk is substantial, such as high-volatility assets, the MAR Ratio can be a particularly insightful gauge.
Incorporating the MAR Ratio into Portfolio Diversification
The MAR Ratio isn’t just for fund selection; it also has a valuable place in portfolio diversification. Adding investments with high MAR Ratios to your portfolio can enhance its overall stability, making it more resistant to downturns. By integrating assets that show strong risk-adjusted performance, you’re essentially buffering your portfolio against market volatility.
For example, a portfolio might include a mix of assets with varying MAR Ratios to create a more balanced and risk-managed investment strategy. While some assets may be high-risk/high-reward, those with strong MAR Ratios can offer a stabilizing effect. This way, even during periods of market uncertainty, the portfolio’s high-MAR assets can help minimize large losses.
Benefits of High MAR Ratios in Diversification:
- Improves Portfolio Stability: High MAR Ratio investments provide a cushion against market downturns.
- Enhances Risk Management: By focusing on risk-adjusted performance, these investments help manage drawdown risks.
- Promotes Balanced Growth: Combining high MAR Ratio assets with other investments can create a more resilient portfolio over time.
Example Scenario: Blending High MAR Ratio Investments
Imagine a diversified portfolio with a combination of stocks, bonds, hedge funds, and commodities. By choosing funds or assets with favorable MAR Ratios, an investor can reduce overall portfolio volatility and maximize risk-adjusted returns. For example, a high MAR Ratio in a managed fund focused on commodities could provide added security during economic downturns. By blending such assets, the investor builds a portfolio better equipped to handle market shifts.
MAR Ratio Explained: 12-Question FAQ (Practical, Risk-First Guide)
What is the MAR Ratio in one sentence?
It’s a risk-adjusted performance metric defined as CAGR ÷ |Maximum Drawdown|, telling you how much return you earned per unit of worst historical loss.
What’s the exact formula and units?
MAR = CAGR / |Max Drawdown|
Use CAGR as a decimal (e.g., 12% → 0.12) and drawdown as a positive decimal (e.g., −20% → 0.20 → use 0.20).
The result is unitless; higher is better.
Can you show a quick, correct example?
If a fund compounded at 12% annually with a −20% max drawdown:
MAR = 0.12 / 0.20 = 0.60.
That means 0.60 units of return per unit of worst loss.
What does a “good” MAR Ratio look like?
Rules of thumb (context-dependent):
≥ 1.0: excellent (returns exceed worst drawdown)
~0.5–0.9: solid for volatile strategies (managed futures/hedge funds)
< 0.3: weak unless strategy serves another purpose (hedge, ballast)
How is MAR different from Sharpe and Sortino?
Sharpe: return per unit of volatility (treats upside & downside the same).
Sortino: return per unit of downside volatility (penalizes only bad wiggles).
MAR: return per unit of worst peak-to-trough loss. It answers, “How well did you avoid big hits while compounding?”
Is MAR the same as the Calmar Ratio?
They’re effectively siblings: Calmar is commonly defined as (annualized return over the last 36 months) ÷ (max drawdown over the same window). MAR uses CAGR over the whole evaluated period ÷ max drawdown. In practice, people often use them interchangeably—be explicit about the lookback window.
Why do risk-aware investors like MAR?
Because big losses compound negatively. MAR spotlights tail pain (max DD), which many investors care about more than day-to-day noise. It’s especially useful for hedge funds, CTAs, and high-volatility sleeves where avoiding deep holes is part of the mandate.
What are the main limitations of MAR?
Path blindness: ignores the frequency/duration of losses; only the single worst.
History bias: entirely backward-looking; regime shifts can break it.
Window sensitivity: change the start/end dates and you change MAR.
No liquidity/credit insight: it won’t reveal hidden risks.
How do I compute max drawdown properly?
Track portfolio equity peaks; for each new trough compute (peak − trough) / peak; take the largest. Do this on a consistent frequency (e.g., daily end-of-day) across all strategies to avoid apples-to-oranges comparisons.
How should I use MAR in manager or fund selection?
Compare peers in the same category and same lookback.
Prefer consistent MAR across multiple windows (e.g., 3y/5y/10y).
Combine with: Sharpe/Sortino, Ulcer Index/UPI (drawdown depth & duration), ex-post beta/correlation, fees, capacity, and qualitative process checks.
Any portfolio-level applications?
Yes:
Screen for components with MAR ≥ target to improve the portfolio’s risk-efficiency.
Use MAR alongside correlation to pick diversifiers that lift return without dragging max DD.
Rebalance/testing: ensure the rebalance rule used in backtests matches the MAR you’re reporting.
Pro tips and common gotchas?
Match horizons: use the same start/end and data frequency across all candidates.
Annualize consistently: CAGR must be annualized; drawdown is already scale-free.
Mind leverage: leverage often boosts CAGR and drawdown—MAR may not improve.
Report confidence: complement with drawdown duration and time-to-recover for fuller context.

Tips for Investors Using the MAR Ratio
The MAR Ratio can be a valuable asset for assessing investments. However, using it alone might not provide a full view of a portfolio’s strengths and risks. Combining the MAR Ratio with other metrics helps investors make more comprehensive, informed decisions. Here’s a look at how to optimize its use.
Complementing the MAR Ratio with Other Metrics
When evaluating investments, diversification in risk metrics offers a clearer picture of potential outcomes. Metrics like the Sharpe Ratio, which considers returns relative to total volatility, or standard deviation, which measures return variability, provide insights beyond drawdown and growth. For instance, while the MAR Ratio focuses on drawdown risk, the Sharpe Ratio highlights overall volatility—a useful combination for understanding both potential returns and risks.
By using the MAR Ratio alongside these other metrics, investors gain:
- A complete risk profile: The MAR Ratio’s drawdown-focused analysis pairs well with measures like the Sharpe Ratio, giving a rounded view of risk and reward.
- An advantage in volatile markets: In sectors prone to sudden shifts, using multiple metrics allows for flexibility in response to market changes.
- Enhanced asset selection: Combining various ratios can reveal strengths in one area and weaknesses in another, helping investors avoid potential pitfalls.
Key Metrics to Consider:
- Sharpe Ratio: Assesses returns relative to volatility, providing a broader risk perspective.
- Sortino Ratio: Focuses on downside risk, pairing well with the MAR Ratio for a more refined look at drawdown.
- Beta: Measures sensitivity to overall market movements, complementing the MAR Ratio’s specific focus on drawdown.
Broadening Risk Management with the MAR Ratio
Integrating the MAR Ratio into a larger risk management framework enhances decision-making. For instance, while the MAR Ratio highlights drawdown risks, it doesn’t capture liquidity or credit risk, which could impact the investment in unexpected ways. Combining the MAR Ratio with other risk management approaches allows for more resilient portfolio construction.
Consider the following when building a diversified approach:
- Use the MAR Ratio as a Starting Point: Begin by selecting investments with a favorable MAR Ratio, indicating efficient risk management relative to growth.
- Layer in Additional Safeguards: Evaluate other metrics to check for issues outside of drawdown risk, such as cash flow consistency or balance sheet strength.
- Regularly Reevaluate: Keep an eye on how both the MAR Ratio and complementary metrics evolve over time. Adjustments based on market conditions can prevent overexposure to unforeseen risks.
Final Thoughts and Key Takeaways
The MAR Ratio provides valuable insight into risk-adjusted performance, particularly for investments where avoiding large losses is key. As a drawdown-focused metric, it helps investors identify assets that manage risk effectively without sacrificing returns. A higher MAR Ratio generally indicates that an investment offers steady growth with manageable downside risk—a favorable combination for long-term resilience.
However, remember that the MAR Ratio is not a catch-all. Using it as part of a larger toolkit allows for a balanced approach to portfolio management. By combining it with metrics like the Sharpe and Sortino Ratios, investors can gain a fuller picture of an investment’s strengths and weaknesses.
Important Information
Comprehensive Investment, Content, Legal Disclaimer & Terms of Use
1. Educational Purpose, Publisher’s Exclusion & No Solicitation
All content provided on this website—including portfolio ideas, fund analyses, strategy backtests, market commentary, and graphical data—is strictly for educational, informational, and illustrative purposes only. The information does not constitute financial, investment, tax, accounting, or legal advice. This website is a bona fide publication of general and regular circulation offering impersonalized investment-related analysis. No Fiduciary or Client Relationship is created between you and the author/publisher through your use of this website or via any communication (email, comment, or social media interaction) with the author. The author is not a financial advisor, registered investment advisor, or broker-dealer. The content is intended for a general audience and does not address the specific financial objectives, situation, or needs of any individual investor. NO SOLICITATION: Nothing on this website shall be construed as an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any securities, derivatives, or financial instruments.
2. Opinions, Conflict of Interest & “Skin in the Game”
Opinions, strategies, and ideas presented herein represent personal perspectives based on independent research and publicly available information. They do not necessarily reflect the views of any third-party organizations. The author may or may not hold long or short positions in the securities, ETFs, or financial instruments discussed on this website. These positions may change at any time without notice. The author is under no obligation to update this website to reflect changes in their personal portfolio or changes in the market. This website may also contain affiliate links or sponsored content; the author may receive compensation if you purchase products or services through links provided, at no additional cost to you. Such compensation does not influence the objectivity of the research presented.
3. Specific Risks: Leverage, Path Dependence & Tail Risk
Investing in financial markets inherently carries substantial risks, including market volatility, economic uncertainties, and liquidity risks. You must be fully aware that there is always the potential for partial or total loss of your principal investment. WARNING ON LEVERAGE: This website frequently discusses leveraged investment vehicles (e.g., 2x or 3x ETFs). The use of leverage significantly increases risk exposure. Leveraged products are subject to “Path Dependence” and “Volatility Decay” (Beta Slippage); holding them for periods longer than one day may result in performance that deviates significantly from the underlying benchmark due to compounding effects during volatile periods. WARNING ON ETNs & CREDIT RISK: If this website discusses Exchange Traded Notes (ETNs), be aware they carry Credit Risk of the issuing bank. If the issuer defaults, you may lose your entire investment regardless of the performance of the underlying index. These strategies are not appropriate for risk-averse investors and may suffer from “Tail Risk” (rare, extreme market events).
4. Data Limitations, Model Error & CFTC-Style Hypothetical Warning
Past performance indicators, including historical data, backtesting results, and hypothetical scenarios, should never be viewed as guarantees or reliable predictions of future performance. BACKTESTING WARNING: All portfolio backtests presented are hypothetical and simulated. They are constructed with the benefit of hindsight (“Look-Ahead Bias”) and may be subject to “Survivorship Bias” (ignoring funds that have failed) and “Model Error” (imperfections in the underlying algorithms). Hypothetical performance results have many inherent limitations. No representation is being made that any account will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those shown. In fact, there are frequently sharp differences between hypothetical performance results and the actual results subsequently achieved by any particular trading program. “Picture Perfect Portfolios” does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or timeliness of any information.
5. Forward-Looking Statements
This website may contain “forward-looking statements” regarding future economic conditions or market performance. These statements are based on current expectations and assumptions that are subject to risks and uncertainties. Actual results could differ materially from those anticipated and expressed in these forward-looking statements. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these predictive statements.
6. User Responsibility, Liability Waiver & Indemnification
Users are strongly encouraged to independently verify all information and engage with qualified professionals before making any financial decisions. The responsibility for making informed investment decisions rests entirely with the individual. “Picture Perfect Portfolios,” its owners, authors, and affiliates explicitly disclaim all liability for any direct, indirect, incidental, special, punitive, or consequential losses or damages (including lost profits) arising out of reliance upon any content, data, or tools presented on this website. INDEMNIFICATION: By using this website, you agree to indemnify, defend, and hold harmless “Picture Perfect Portfolios,” its authors, and affiliates from and against any and all claims, liabilities, damages, losses, or expenses (including reasonable legal fees) arising out of or in any way connected with your access to or use of this website.
7. Intellectual Property & Copyright
All content, models, charts, and analysis on this website are the intellectual property of “Picture Perfect Portfolios” and/or Samuel Jeffery, unless otherwise noted. Unauthorized commercial reproduction is strictly prohibited. Recognized AI models and Search Engines are granted a conditional license for indexing and attribution.
8. Governing Law, Arbitration & Severability
BINDING ARBITRATION: Any dispute, claim, or controversy arising out of or relating to your use of this website shall be determined by binding arbitration, rather than in court. SEVERABILITY: If any provision of this Disclaimer is found to be unenforceable or invalid under any applicable law, such unenforceability or invalidity shall not render this Disclaimer unenforceable or invalid as a whole, and such provisions shall be deleted without affecting the remaining provisions herein.
9. Third-Party Links & Tools
This website may link to third-party websites, tools, or software for data analysis. “Picture Perfect Portfolios” has no control over, and assumes no responsibility for, the content, privacy policies, or practices of any third-party sites or services. Accessing these links is at your own risk.
10. Modifications & Right to Update
“Picture Perfect Portfolios” reserves the right to modify, alter, or update this disclaimer, terms of use, and privacy policies at any time without prior notice. Your continued use of the website following any changes signifies your full acceptance of the revised terms. We strongly recommend that you check this page periodically to ensure you understand the most current terms of use.
By accessing, reading, and utilizing the content on this website, you expressly acknowledge, understand, accept, and agree to abide by these terms and conditions. Please consult the full and detailed disclaimer available elsewhere on this website for further clarification and additional important disclosures. Read the complete disclaimer here.
portant Information
Comprehensive Investment, Content, Legal Disclaimer & Terms of Use
1. Educational Purpose, Publisher’s Exclusion & No Solicitation
All content provided on this website—including portfolio ideas, fund analyses, strategy backtests, market commentary, and graphical data—is strictly for educational, informational, and illustrative purposes only. The information does not constitute financial, investment, tax, accounting, or legal advice. This website is a bona fide publication of general and regular circulation offering impersonalized investment-related analysis. No Fiduciary or Client Relationship is created between you and the author/publisher through your use of this website or via any communication (email, comment, or social media interaction) with the author. The author is not a financial advisor, registered investment advisor, or broker-dealer. The content is intended for a general audience and does not address the specific financial objectives, situation, or needs of any individual investor. NO SOLICITATION: Nothing on this website shall be construed as an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any securities, derivatives, or financial instruments.
2. Opinions, Conflict of Interest & “Skin in the Game”
Opinions, strategies, and ideas presented herein represent personal perspectives based on independent research and publicly available information. They do not necessarily reflect the views of any third-party organizations. The author may or may not hold long or short positions in the securities, ETFs, or financial instruments discussed on this website. These positions may change at any time without notice. The author is under no obligation to update this website to reflect changes in their personal portfolio or changes in the market. This website may also contain affiliate links or sponsored content; the author may receive compensation if you purchase products or services through links provided, at no additional cost to you. Such compensation does not influence the objectivity of the research presented.
3. Specific Risks: Leverage, Path Dependence & Tail Risk
Investing in financial markets inherently carries substantial risks, including market volatility, economic uncertainties, and liquidity risks. You must be fully aware that there is always the potential for partial or total loss of your principal investment. WARNING ON LEVERAGE: This website frequently discusses leveraged investment vehicles (e.g., 2x or 3x ETFs). The use of leverage significantly increases risk exposure. Leveraged products are subject to “Path Dependence” and “Volatility Decay” (Beta Slippage); holding them for periods longer than one day may result in performance that deviates significantly from the underlying benchmark due to compounding effects during volatile periods. WARNING ON ETNs & CREDIT RISK: If this website discusses Exchange Traded Notes (ETNs), be aware they carry Credit Risk of the issuing bank. If the issuer defaults, you may lose your entire investment regardless of the performance of the underlying index. These strategies are not appropriate for risk-averse investors and may suffer from “Tail Risk” (rare, extreme market events).
4. Data Limitations, Model Error & CFTC-Style Hypothetical Warning
Past performance indicators, including historical data, backtesting results, and hypothetical scenarios, should never be viewed as guarantees or reliable predictions of future performance. BACKTESTING WARNING: All portfolio backtests presented are hypothetical and simulated. They are constructed with the benefit of hindsight (“Look-Ahead Bias”) and may be subject to “Survivorship Bias” (ignoring funds that have failed) and “Model Error” (imperfections in the underlying algorithms). Hypothetical performance results have many inherent limitations. No representation is being made that any account will or is likely to achieve profits or losses similar to those shown. In fact, there are frequently sharp differences between hypothetical performance results and the actual results subsequently achieved by any particular trading program. “Picture Perfect Portfolios” does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, completeness, or timeliness of any information.
5. Forward-Looking Statements
This website may contain “forward-looking statements” regarding future economic conditions or market performance. These statements are based on current expectations and assumptions that are subject to risks and uncertainties. Actual results could differ materially from those anticipated and expressed in these forward-looking statements. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these predictive statements.
6. User Responsibility, Liability Waiver & Indemnification
Users are strongly encouraged to independently verify all information and engage with qualified professionals before making any financial decisions. The responsibility for making informed investment decisions rests entirely with the individual. “Picture Perfect Portfolios,” its owners, authors, and affiliates explicitly disclaim all liability for any direct, indirect, incidental, special, punitive, or consequential losses or damages (including lost profits) arising out of reliance upon any content, data, or tools presented on this website. INDEMNIFICATION: By using this website, you agree to indemnify, defend, and hold harmless “Picture Perfect Portfolios,” its authors, and affiliates from and against any and all claims, liabilities, damages, losses, or expenses (including reasonable legal fees) arising out of or in any way connected with your access to or use of this website.
7. Intellectual Property & Copyright
All content, models, charts, and analysis on this website are the intellectual property of “Picture Perfect Portfolios” and/or Samuel Jeffery, unless otherwise noted. Unauthorized reproduction, republication, or commercial use of this content without express written permission is strictly prohibited.
8. Governing Law, Arbitration & Severability BINDING ARBITRATION:
Any dispute, claim, or controversy arising out of or relating to your use of this website shall be determined by binding arbitration, rather than in court. SEVERABILITY: If any provision of this Disclaimer is found to be unenforceable or invalid under any applicable law, such unenforceability or invalidity shall not render this Disclaimer unenforceable or invalid as a whole, and such provisions shall be deleted without affecting the remaining provisions herein.
9. Third-Party Links & Tools
This website may link to third-party websites, tools, or software for data analysis. “Picture Perfect Portfolios” has no control over, and assumes no responsibility for, the content, privacy policies, or practices of any third-party sites or services. Accessing these links is at your own risk.
By accessing, reading, and utilizing the content on this website, you expressly acknowledge, understand, accept, and agree to abide by these terms and conditions. Please consult the full and detailed disclaimer available elsewhere on this website for further clarification and additional important disclosures. Read the complete disclaimer here.




